What is a Cricket Pitch?

A cricket pitch is the core area where the game is played. It’s a rectangular, flat stretch of trimmed grass, often influencing the outcome of a match based on its condition. Bowlers try to exploit its nuances to deliver challenging balls, while batsmen attempt to score runs. The pitch’s unique characteristics, such as its dryness or moisture content, can favor either pacers or spinners.
Cricket Pitch Dimensions
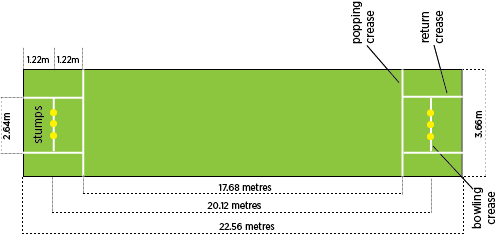
The cricket pitch is a 22-yard long strip in the center of the field, which equals 66 feet in length and 10 feet in width. Measured in meters, the pitch is 20.12 meters long and 3.05 meters wide. It is typically covered with short grass, but pitches can also be dry, dusty, or have very little grass, depending on the playing conditions.
Read More:- All You Need to Know About Reserve Day in the IPL
At either end of the pitch, the bowling crease spans 2.64 meters, marking the boundary for bowlers. The rectangular “Protected Area” lies in the middle of the pitch, running parallel to the popping creases. This two-foot-wide strip is off-limits to bowlers, helping preserve the pitch and maintain fair play.
Protected Area on a Cricket Pitch

The “protected area” or “danger zone” is a rectangular section, two feet wide, located in the center of the pitch. It starts five feet from each popping crease. Bowlers are restricted from stepping on this zone during their follow-through to prevent creating rough patches, which could lead to unpredictable ball bounce and turn, affecting the game.
If a bowler steps into the protected area twice, umpires issue a warning. A third violation results in the bowler being banned from bowling for the remainder of the innings.
Main Types of Cricket Pitches
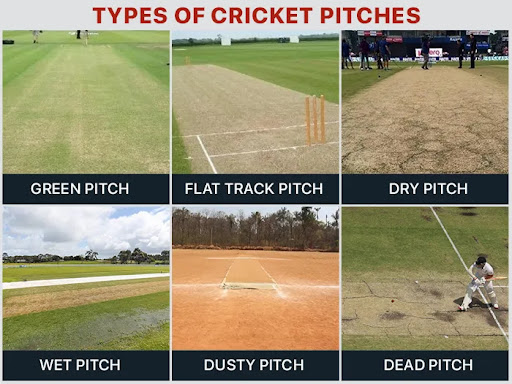
The nature of the pitch can greatly influence the course of a cricket match. There are three primary types of pitches used in international cricket, each offering distinct challenges for bowlers and batsmen.
1. Green Pitch
A green pitch, also called a “green top,” is covered with a longer layer of grass than usual. It favors fast bowlers, as the ball swings and seams unpredictably off the surface. These pitches, often found in places like England, retain moisture, making it difficult for batsmen to settle in. Green tops are more common in Test and ODI cricket.
2. Dry Pitch
Dry pitches lack moisture and often have cracks. These are common in the subcontinent. Batsmen may find it easier to score on dry pitches because the ball doesn’t bounce as much. However, spin bowlers become more dangerous as the game progresses, as the dry surface helps them get a better grip, enhancing spin.
3. Flat Pitch
Flat pitches are generally easy for batsmen to play on, as they lack grass and cracks. The ball tends to bounce predictably, making it easier to score runs. Bowlers, especially pacers, struggle to extract movement from these surfaces, often leading to high-scoring matches.
Maintaining a Cricket Pitch

The condition of a cricket pitch can change during a match, and proper maintenance ensures a fair and balanced contest. Here are some key steps involved in maintaining a cricket pitch.
1. Covering
To protect the pitch from rain or dew, covers are placed over it. This can affect the ball’s behavior, sparking debate over fair play. According to Law 11 of cricket, a pitch can only be entirely covered with prior agreement. Covers are typically removed before play begins each day, and during wet conditions, bowlers’ run-ups may be covered to keep them dry.
2. Rolling
Rolling compacts the soil, reduces the amount of grass, and smooths the pitch surface. This helps the pitch behave consistently during play. The batting captain can request the pitch to be rolled for up to seven minutes before each innings or at the start of the day’s play.
3. Sweeping
Sweeping the pitch clears away any debris that could affect the ball’s bounce or rolling process. Groundsmen sweep the pitch before rolling, between innings, and at the start of each day’s play.
4. Securing Footing
Players are allowed to secure their footholds on the pitch using sawdust, especially when the ground is wet. Batsmen often use their bats to tap the pitch and firm up their stance, provided it doesn’t cause damage.
5. Maintaining Foot Holes
During wet conditions or extended matches, umpires monitor the foot holes created by bowlers and batsmen to ensure they don’t disrupt the game. In matches lasting more than two days, umpires may authorize the repair of foot holes or the use of quick-setting fillers before play resumes.
FAQs
What is the pitch length in the IPL?
The length of the pitch in IPL is the same as international cricket—20.12 meters in length and 3.05 meters in width.
What is the measurement of a cricket pitch in meters?
A cricket pitch measures 20.12 meters in length and 3.05 meters in width.
What is the measurement of a cricket pitch length in feet?
A cricket pitch measures 66 feet in length and 10 feet in width.
Read More:- Cameron Green in IPL 2024: Playing Status, Price & More
